动态路由
一般情况下,我们的微服务接口在创建的时候就已经决定了路径映射,当我们的服务接口路径发生了改变的时候,按照前面在zuul配置文件里面配置的话需要重启网关,因为zuul启动之后这些路由规则会被加载到内存里面。但是我们一般不会轻易的下线服务然后重新上线。
一般来说我们是需要这些路由规则是可以动态配置,仅把路由规则写在配置文件里面,灵活度不足。常见的由两种解决方案:
- Spring Cloud Config + Bus:动态刷新配置文件。这种方式是不用zuul来维护映射规则,可以随时修改,随时生效。不足的是需要集合额外的组件,复杂度上升,系统的可用性也会随之降低。
- 重写zuul配置读取方式:采取时间刷新机制,从数据库读取路由规则。因此需要把zuul的路由规则写到数据库里面,因此也需要提供一个管理界面,灵活度较高。例如:
apache shenyu网关的实现。
通常是会采用Spring Cloud Config + Bus这种方式,也是Spring Cloud生态推崇的,不过也有局限性。建议使用第二种方式。
zuul动态路由刷新原理
DiscoveryClientRouteLocator
从数据库读取到路由规则后需要刷新到内存,所以zuul路由规则相关的几个核心需要掌握。
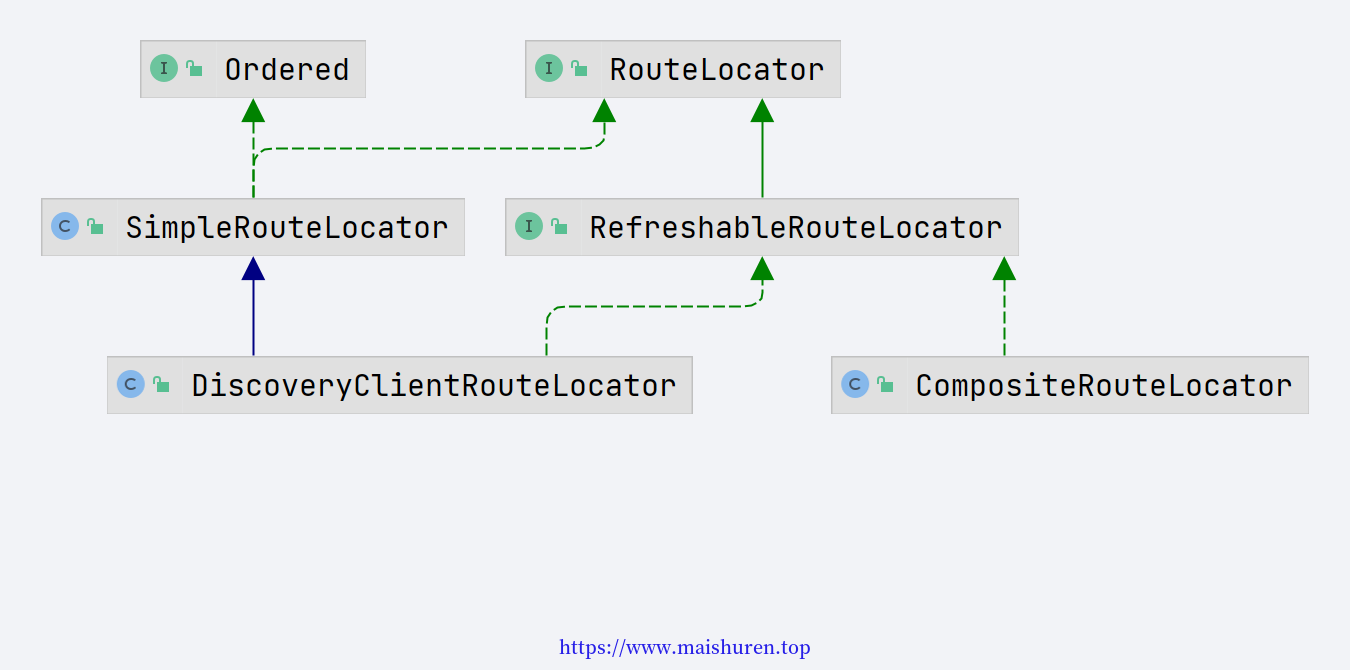
DiscoveryClientRouteLocator是zuul对路由配置信息读取和新节点注册变更的操作类。locateRoutes()是重写了父类SimpleRputeLocator的方法,重写了规则。该方法主要是将配置文件中的路由规则封装到LinkedHashMap<String, ZuulProperties.ZuulRoute>,Key为path路径,值是ZuulRoute路由信息。所以配置文件中配置的路由会被封装成ZuulRoute对象并放到LinkedHashMap中。
refresh()方法则是刷新zuul中路由信息的方法。doRefresh()方法是来自父类SimpleRouteLocator,因此要实现从数据库读取路由规则并刷新到zuul内存,可以仿照它的实现。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
public class DiscoveryClientRouteLocator extends SimpleRouteLocator implements RefreshableRouteLocator {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(DiscoveryClientRouteLocator.class);
public static final String DEFAULT_ROUTE = "/**";
private DiscoveryClient discovery;
private ZuulProperties properties;
private ServiceRouteMapper serviceRouteMapper;
...
public void addRoute(String path, String location) {
this.properties.getRoutes().put(path, new ZuulProperties.ZuulRoute(path, location));
this.refresh();
}
public void addRoute(ZuulProperties.ZuulRoute route) {
this.properties.getRoutes().put(route.getPath(), route);
this.refresh();
}
@Override
protected LinkedHashMap<String, ZuulProperties.ZuulRoute> locateRoutes() {
...
}
@Override
public void refresh() {
this.doRefresh();
}
protected String mapRouteToService(String serviceId) {
return this.serviceRouteMapper.apply(serviceId);
}
protected void addConfiguredRoutes(Map<String, ZuulProperties.ZuulRoute> routes) {
...
}
}
|
SimpleRouteLocator
SimpleRouteLocator此类实现了RouteLocator接口,对读取配置文件信息做了一下基本处理,提供了doRefresh()和locateRoutes()方法给子类实现刷新策略和路由规则加载策略。ptotected修饰了这两个方法,为了让子类不用维护此类的一些成员变量就能够实现刷新和读取路由的功能。
并且如果调用doRefresh()方法,需要实现RefreshableRouteLocator接口。locateRoutes()方法默认是一个静态的映射读取方法,如果需要动态读取加载路由映射,需要子类来实现此方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
public class SimpleRouteLocator implements RouteLocator, Ordered {
...
protected void doRefresh() {
this.routes.set(this.locateRoutes());
}
protected Map<String, ZuulProperties.ZuulRoute> locateRoutes() {
LinkedHashMap<String, ZuulProperties.ZuulRoute> routesMap = new LinkedHashMap();
Iterator var2 = this.properties.getRoutes().values().iterator();
while(var2.hasNext()) {
ZuulProperties.ZuulRoute route = (ZuulProperties.ZuulRoute)var2.next();
routesMap.put(route.getPath(), route);
}
return routesMap;
}
}
|
ZuulServerAutoConfiguration自动配置
了解ZuulServerAutoConfiguration的自动配置了各种过滤器监听器以及其他的功能,在这类里面可以看到Zuul的功能组件。Zuul在注册中心新增服务后刷新监听器也是在这里注册的,底层是采用Spring的ApplicationListener监听器来实现的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
|
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ZuulProperties.class})
@ConditionalOnClass({ZuulServlet.class})
@ConditionalOnBean({ZuulServerMarkerConfiguration.Marker.class})
public class ZuulServerAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired
protected ZuulProperties zuulProperties;
@Autowired
protected ServerProperties server;
@Autowired(
required = false
)
private ErrorController errorController;
public ZuulServerAutoConfiguration() {
}
...
@Bean
public ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> zuulRefreshRoutesListener() {
return new ZuulRefreshListener();
}
private static class ZuulRefreshListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> {
@Autowired
private ZuulHandlerMapping zuulHandlerMapping;
private HeartbeatMonitor heartbeatMonitor;
private ZuulRefreshListener() {
this.heartbeatMonitor = new HeartbeatMonitor();
}
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (!(event instanceof ContextRefreshedEvent) && !(event instanceof RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent) && !(event instanceof RoutesRefreshedEvent) && !(event instanceof InstanceRegisteredEvent)) {
if (event instanceof ParentHeartbeatEvent) {
ParentHeartbeatEvent e = (ParentHeartbeatEvent)event;
this.resetIfNeeded(e.getValue());
} else if (event instanceof HeartbeatEvent) {
HeartbeatEvent e = (HeartbeatEvent)event;
this.resetIfNeeded(e.getValue());
}
} else {
this.reset();
}
}
private void resetIfNeeded(Object value) {
if (this.heartbeatMonitor.update(value)) {
this.reset();
}
}
private void reset() {
this.zuulHandlerMapping.setDirty(true);
}
}
...
}
|
从ZuulRefreshListener的源码可以看到,该监听器只接收三种事件:ContextRefreshedEvent(Spring上下文刷新事件)、RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent(Scope刷新事件,@Value)、RoutesRefreshedEvent(路由刷新事件)以及InstanceRegisterEvent(服务注册事件)。通过接收这四个事件通知去刷新路由映射规则;此外心跳事件也会触发通过心跳监听器HeartbeatMonitor也会触发这个动作。
ZuulHandlerMapping映射处理器
这个类是将本地配置的映射关系映射到远程的过程控制器,与刷新事件相关的是一个setDirty()方法,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public class ZuulHandlerMapping extends AbstractUrlHandlerMapping {
private final RouteLocator routeLocator;
private final ZuulController zuul;
private ErrorController errorController;
private PathMatcher pathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
private volatile boolean dirty = true;
...
public void setDirty(boolean dirty) {
this.dirty = dirty;
if (this.routeLocator instanceof RefreshableRouteLocator) {
((RefreshableRouteLocator)this.routeLocator).refresh();
}
}
...
}
|
dirty这个属性是用来控制当前是否需要重新加载映射配置信息的标记,在zuul每次进行路由的时候都会检查这个值,如果设置为true,就会触发配置信息的重新接在,加载完成后再将其设置为false。启动刷新动作必须要实现RefreshableRouteLocator接口。
实现思路
在实现zuul动态路由的时候,需要重写SimpleRouteLocator的locateRoutes()方法,并且实现RefreshableRouteLocator接口的refresh()方法,再在内部调用doRefresh()方法,就可以实现zuul内部事件触发的自定义动态路由加载器。
事实上是我们会重写onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event)方法,使用手动触发刷新路由映射规则配置。这样子页面上配置保存到数据库,然后发布事件触发。
基于数据库的动态路由实现
基于数据库的实现本章节会讲述实现核心原理,更好的实现是需要编写一个网关配置的后台系统。不过核心原理是一样的。
Zuul Server
zuul网关引入依赖:这里数据库使用MySQL,ORM是使用spring-data-jpa。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
配置文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
server:
port: 88
spring:
application:
name: zuul-server
datasource:
username: root
password: root123456
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jpa:
show-sql: true
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update
naming:
physical-strategy: org.springframework.boot.orm.jpa.hibernate.SpringPhysicalNamingStrategy
properties:
hibernate:
dialect: org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL57Dialect
storage_engine: innodb
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://${eureka.host:127.0.0.1}:${eureka.port:8671}/eureka/
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true
|
实体类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
@Entity
@Table(name = "routing_rule")
public class RoutingRule {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String path;
private String serviceId;
private String url;
private Integer stripPrefix;
private Integer retryable;
private Integer enabled;
private String description;
...省略getter setter
}
|
RoutingRuleDao:
1
2
3
|
@Repository
public interface RoutingRuleDao extends JpaRepository<RoutingRule, Long> {
}
|
Service层:
1
2
3
|
public interface RoutingRuleService {
Map<String, ZuulProperties.ZuulRoute> findAllRoutes();
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
@Service
public class RoutingRuleServiceImpl implements RoutingRuleService {
@Autowired
private RoutingRuleDao routingRuleDao;
@Override
public Map<String, ZuulProperties.ZuulRoute> findAllRoutes() {
RoutingRule routingRule = new RoutingRule();
routingRule.setEnabled(1);
Example<RoutingRule> example = Example.of(routingRule);
List<RoutingRule> routingRuleList = routingRuleDao.findAll(example);
Map<String, ZuulProperties.ZuulRoute> zuulRouteMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
routingRuleList.stream().filter(item -> StringUtils.isNotBlank(item.getPath()))
.forEach(item -> {
ZuulProperties.ZuulRoute zuulRoute = new ZuulProperties.ZuulRoute();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(item, zuulRoute);
zuulRoute.setId(String.valueOf(item.getId()));
zuulRouteMap.put(item.getPath(), zuulRoute);
});
return zuulRouteMap;
}
}
|
实现动态路由配置:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
public class DynamicZuulRouteLocator extends SimpleRouteLocator implements RefreshableRouteLocator {
private ZuulProperties zuulProperties;
private RoutingRuleService routingRuleService;
public DynamicZuulRouteLocator(String servletPath, ZuulProperties properties, RoutingRuleService routingRuleService) {
super(servletPath, properties);
this.zuulProperties = properties;
this.routingRuleService = routingRuleService;
}
@Override
public void refresh() {
doRefresh();
}
@Override
protected Map<String, ZuulProperties.ZuulRoute> locateRoutes() {
LinkedHashMap<String, ZuulProperties.ZuulRoute> routesMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
routesMap.putAll(super.locateRoutes());
routesMap.putAll(routingRuleService.findAllRoutes());
LinkedHashMap<String, ZuulProperties.ZuulRoute> values = new LinkedHashMap<>();
routesMap.forEach((key, value) -> {
String path = key;
if (!path.startsWith("/")) {
path = "/" + path;
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.zuulProperties.getPrefix())) {
path = this.zuulProperties.getPrefix() + path;
if (!path.startsWith("/")) {
path = "/" + path;
}
}
values.put(path, value);
});
return values;
}
}
|
注入到Spring容器:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
@Configuration
public class ZuulRouteConfig {
@Autowired
private ZuulProperties zuulProperties;
@Autowired
private ServerProperties serverProperties;
@Autowired
private RoutingRuleService routingRuleService;
@Bean
public DynamicZuulRouteLocator routeLocator() {
DynamicZuulRouteLocator routeLocator = new DynamicZuulRouteLocator(serverProperties.getServlet().getContextPath(),
zuulProperties, routingRuleService);
return routeLocator;
}
}
|
编写cloud-serice-b
maven依赖:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- springboot web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!--不用Tomcat,使用undertow -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-undertow</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.undertow</groupId>
<artifactId>undertow-servlet</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
配置文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
server:
port: 8081
spring:
application:
name: service-b
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://${eureka.host:127.0.0.1}:${eureka.port:8671}/eureka/
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true
|
编写Controller:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
@RestController
@RequestMapping("hello")
public class ServiceBController {
@GetMapping("hi")
public Object hi(String name) {
return "hi " + name + "! This service b";
}
}
|
启动类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@SpringBootApplication
public class ServiceBApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ServiceBApplication.class);
}
}
|
启动测试
插入准备好的数据
1
2
3
4
|
insert into `routing_rule`(`path`,`service_id`,`url`,`strip_prefix`,`retryable`,`enabled`,`description`) values ('/baidu/**',NULL,'http://www.baidu.com',1,0,1,'重定向到百度首页');
insert into `routing_rule`(`path`,`service_id`,`url`,`strip_prefix`,`retryable`,`enabled`,`description`) values ('/client/**',NULL,'http://localhost:7070',1,0,1,'url');
insert into `routing_rule`(`path`,`service_id`,`url`,`strip_prefix`,`retryable`,`enabled`,`description`) values ('/service-b/**','service-b',NULL,1,0,1,'serviceId');
SELECT * FROM `routing_rule`;
|
浏览器访问:
http://localhost:88/service-b/hello/hi?name=jack
接口返回:
hi jack! This service b
ZuulRefreshListener解析
因为我们再zuul的配置文件中配置了sql打印,在我们没有任何操作的时候,日志会定时打印查询路由的sql。很明显有个像定时一样的在加载路由映射。
DynamicZuulRouteLocator的locateRoutes()是由doRefresh()方法调用,所以从refresh()的调用进行源码追踪,最后会追踪到到ZuulServerAutoConfiguration里的监听器ZuulRefreshListener,源码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
|
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ ZuulProperties.class })
@ConditionalOnClass(ZuulServlet.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(ZuulServerMarkerConfiguration.Marker.class)
// Make sure to get the ServerProperties from the same place as a normal web app would
// FIXME @Import(ServerPropertiesAutoConfiguration.class)
public class ZuulServerAutoConfiguration {
...
@Bean
public ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> zuulRefreshRoutesListener() {
return new ZuulRefreshListener();
}
@Bean
@Primary
public CompositeRouteLocator primaryRouteLocator(
Collection<RouteLocator> routeLocators) {
return new CompositeRouteLocator(routeLocators);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(SimpleRouteLocator.class)
public SimpleRouteLocator simpleRouteLocator() {
return new SimpleRouteLocator(this.server.getServlet().getServletPrefix(),
this.zuulProperties);
}
@Bean
public ZuulController zuulController() {
return new ZuulController();
}
@Bean
public ZuulHandlerMapping zuulHandlerMapping(RouteLocator routes) {
ZuulHandlerMapping mapping = new ZuulHandlerMapping(routes, zuulController());
mapping.setErrorController(this.errorController);
return mapping;
}
...
private static class ZuulRefreshListener
implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> {
@Autowired
private ZuulHandlerMapping zuulHandlerMapping;
private HeartbeatMonitor heartbeatMonitor = new HeartbeatMonitor();
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ContextRefreshedEvent
|| event instanceof RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent
|| event instanceof RoutesRefreshedEvent
|| event instanceof InstanceRegisteredEvent) {
reset();
}
else if (event instanceof ParentHeartbeatEvent) {
ParentHeartbeatEvent e = (ParentHeartbeatEvent) event;
resetIfNeeded(e.getValue());
}
else if (event instanceof HeartbeatEvent) {
HeartbeatEvent e = (HeartbeatEvent) event;
resetIfNeeded(e.getValue());
}
}
private void resetIfNeeded(Object value) {
if (this.heartbeatMonitor.update(value)) {
reset();
}
}
private void reset() {
this.zuulHandlerMapping.setDirty(true);
}
}
}
|
可以看到reset()方法会调用zuulHandlerMapping的setDirty()方法从而触发 refresh,所以这就是上面章节所说的setDirty()的重点。
源码你可以看到除了那四个刷新事件外,还有心跳事件也会触发。所以通过开发工具下载该源码然后,在onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event)方法里面打个断点,看一下到底是什么事件触发路由刷新。
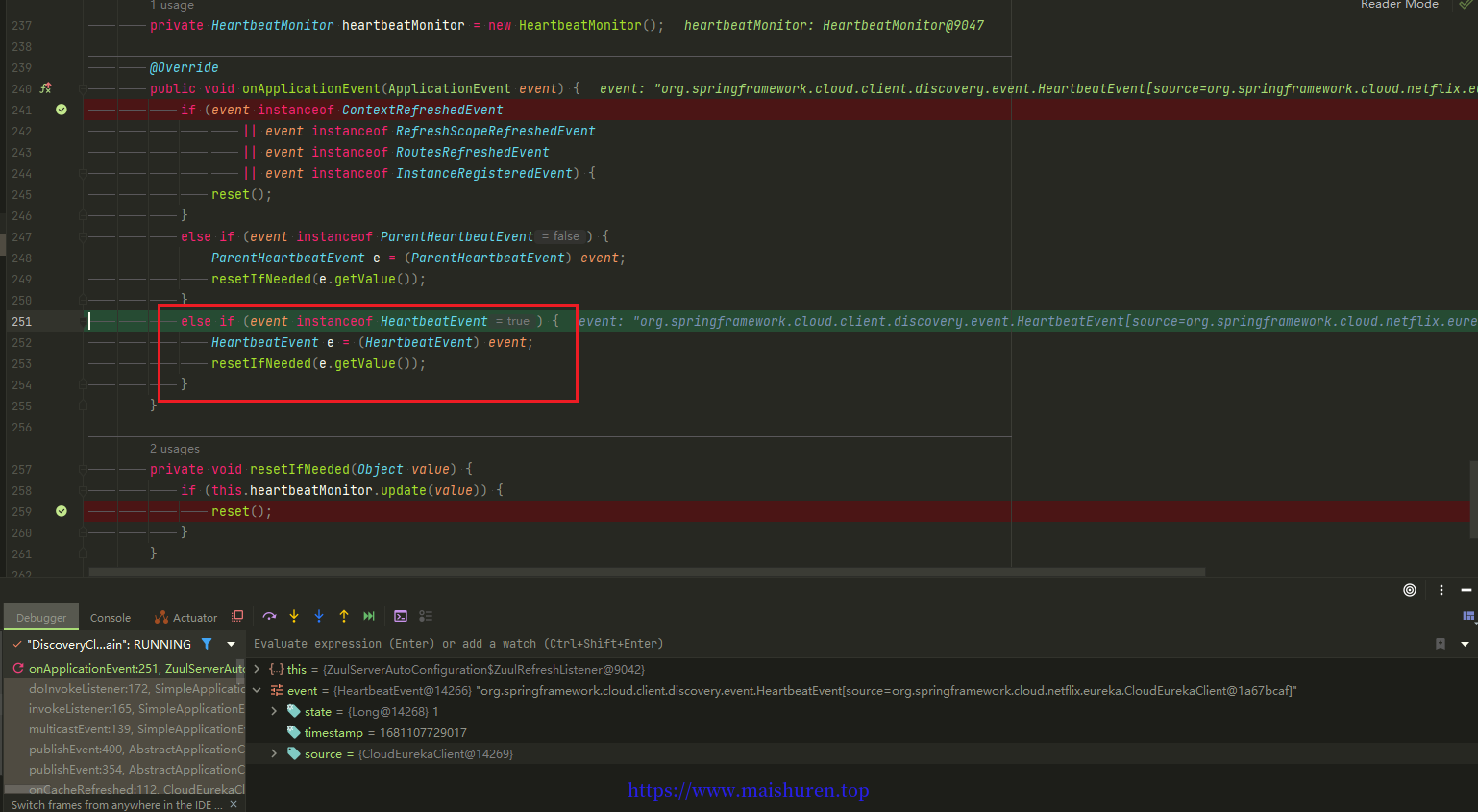
从上图可以看到,触发路由刷新的事件是HeartbeatEvent,这就很明显了,是不断的心跳发布了心跳事件,而且过来的value是个Long类型,是一个不断叠加的值。所以每次心跳事件都会触发路由刷新。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
public class HeartbeatMonitor {
private AtomicReference<Object> latestHeartbeat = new AtomicReference<>();
/**
* @param value the latest heartbeat
* @return true if the state changed
*/
public boolean update(Object value) {
Object last = this.latestHeartbeat.get();
if (value != null && !value.equals(last)) {
return this.latestHeartbeat.compareAndSet(last, value);
}
return false;
}
}
|
总结
动态路由配置是很多网关在实际项目中需要用到的功能。但是像Zuul、Spring Cloud Gateway这些是没有提供完善的功能,使得需要开发者自己去实现。不像Apache Shenyu网关提供了很多开箱即用的功能,如果开发量较大,可以结合实际项目调研一下Apache Shenyu。
本文提到了手动刷新路由配置并且DynamicZuulRouteLocator还有可以优化的地方,但是写到这里本文的篇幅已经不短了,这一部分将在下一篇中把坑给填了。


