默认的配置文件
|
|
- user:设置nginx服务的系统使用用户
- worker_processes:工作进程数
- error_log:nginx的错误日志
- pid:nginx服务启动时候pid
- events:
- worker_connections:每个进程允许最大连接数
- use:工作进程数
- server:
- listen 80 监听服务器80端口
- server_name 可配置域名
- location /:根目录
- root & index:默认访问页面
- error_page: 错误页面,500 502 503 504 404这些状态码都会跳转到/50x.html
- location = /50x.html:响应50x.html的访问,根目录下的50x.html
- keepalive_timeout:客户端超时时间
- include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf:引入配置文件,一般一个配置文件一个server
日志格式log_format
|
|
1.Http变量:arg_PARAMETER、http_HEADER、sent_http_HEADER
eg:log_format main ‘$arg_PARAMETER $http_HEADER $sent_http_HEADER’
2.内置变量:
内置变量存放在 ngx_http_core_module 模块中,变量的命名方式和apache 服务器变量是一致的。总而言之,这些变量代表着客户端请求头的内容。下面是nginx支持的内置变量:
$arg_name
请求中的的参数名,即“?”后面的arg_name=arg_value形式的arg_name
$args
请求中的参数值
$binary_remote_addr
客户端地址的二进制形式, 固定长度为4个字节
$body_bytes_sent
传输给客户端的字节数,响应头不计算在内;这个变量和Apache的mod_log_config模块中的“%B”参数保持兼容
$bytes_sent
传输给客户端的字节数 (1.3.8, 1.2.5)
$connection
TCP连接的序列号 (1.3.8, 1.2.5)
$connection_requests
TCP连接当前的请求数量 (1.3.8, 1.2.5)
$content_length
“Content-Length” 请求头字段
$content_type
“Content-Type” 请求头字段
$cookie_name
cookie名称
$document_root
当前请求的文档根目录或别名
$document_uri
同 $uri
$host
优先级如下:HTTP请求行的主机名>”HOST”请求头字段>符合请求的服务器名
$hostname
主机名
$http_name
匹配任意请求头字段; 变量名中的后半部分“name”可以替换成任意请求头字段,如在配置文件中需要获取http请求头:“Accept-Language”,那么将“-”替换为下划线,大写字母替换为小写,形如:$http_accept_language即可。
**$https **
如果开启了SSL安全模式,值为“on”,否则为空字符串。
$is_args
如果请求中有参数,值为“?”,否则为空字符串。
$limit_rate
用于设置响应的速度限制,详见 limit_rate。
$msec
当前的Unix时间戳 (1.3.9, 1.2.6)
$nginx_version
nginx版本
$pid
工作进程的PID
$pipe
如果请求来自管道通信,值为“p”,否则为“.” (1.3.12, 1.2.7)
$proxy_protocol_addr
获取代理访问服务器的客户端地址,如果是直接访问,该值为空字符串。(1.5.12)
$query_string
同 $args
$realpath_root
当前请求的文档根目录或别名的真实路径,会将所有符号连接转换为真实路径。
$remote_addr
客户端地址
$remote_port
客户端端口
$remote_user
用于HTTP基础认证服务的用户名
$request
代表客户端的请求地址
$request_body
客户端的请求主体
此变量可在location中使用,将请求主体通过proxy_pass, fastcgi_pass, uwsgi_pass, 和 scgi_pass传递给下一级的代理服务器。
$request_body_file
将客户端请求主体保存在临时文件中。文件处理结束后,此文件需删除。如果需要之一开启此功能,需要设置client_body_in_file_only。如果将次文件传递给后端的代理服务器,需要禁用request body,即设置proxy_pass_request_body off,fastcgi_pass_request_body off, uwsgi_pass_request_body off, or scgi_pass_request_body off 。
$request_completion
如果请求成功,值为”OK”,如果请求未完成或者请求不是一个范围请求的最后一部分,则为空。
$request_filename
当前连接请求的文件路径,由root或alias指令与URI请求生成。
$request_length
请求的长度 (包括请求的地址, http请求头和请求主体) (1.3.12, 1.2.7)
$request_method
HTTP请求方法,通常为“GET”或“POST”
$request_time
处理客户端请求使用的时间 (1.3.9, 1.2.6); 从读取客户端的第一个字节开始计时。
$request_uri
这个变量等于包含一些客户端请求参数的原始URI,它无法修改,请查看$uri更改或重写URI,不包含主机名,例如:”/cnphp/test.php?arg=freemouse”。
$scheme
请求使用的Web协议, “http” 或 “https”
$sent_http_name
可以设置任意http响应头字段; 变量名中的后半部分“name”可以替换成任意响应头字段,如需要设置响应头Content-length,那么将“-”替换为下划线,大写字母替换为小写,形如:$sent_http_content_length 4096即可。
$server_addr
服务器端地址,需要注意的是:为了避免访问linux系统内核,应将ip地址提前设置在配置文件中。
$server_name
服务器名,www.cnphp.info
$server_port
服务器端口
$server_protocol
服务器的HTTP版本, 通常为 “HTTP/1.0” 或 “HTTP/1.1”
$status
HTTP响应代码 (1.3.2, 1.2.2)
$tcpinfo_rtt, $tcpinfo_rttvar, $tcpinfo_snd_cwnd, $tcpinfo_rcv_space
客户端TCP连接的具体信息
$time_iso8601
服务器时间的ISO 8610格式 (1.3.12, 1.2.7)
**$time_local $arg_name **
请求中的的参数名,即“?”后面的arg_name=arg_value形式的arg_name
$args
请求中的参数值
$binary_remote_addr
客户端地址的二进制形式, 固定长度为4个字节
$body_bytes_sent
传输给客户端的字节数,响应头不计算在内;这个变量和Apache的mod_log_config模块中的“%B”参数保持兼容
$bytes_sent
传输给客户端的字节数 (1.3.8, 1.2.5)
$connection
TCP连接的序列号 (1.3.8, 1.2.5)
$connection_requests
TCP连接当前的请求数量 (1.3.8, 1.2.5)
**$content_lengt **
“Content-Length” 请求头字段
$content_type
“Content-Type” 请求头字段
**$cookie_name **
cookie名称
$document_root
当前请求的文档根目录或别名
$document_uri
同 $uri
$host
优先级如下:HTTP请求行的主机名>”HOST”请求头字段>符合请求的服务器名
$hostname
主机名
$http_name
匹配任意请求头字段; 变量名中的后半部分“name”可以替换成任意请求头字段,如在配置文件中需要获取http请求头:“Accept-Language”,那么将“-”替换为下划线,大写字母替换为小写,形如:$http_accept_language即可。
$https
如果开启了SSL安全模式,值为“on”,否则为空字符串。
$is_args
如果请求中有参数,值为“?”,否则为空字符串。
$limit_rate
用于设置响应的速度限制,详见 limit_rate。
$msec
当前的Unix时间戳 (1.3.9, 1.2.6)
$nginx_version
nginx版本
$pid
工作进程的PID
$pipe
如果请求来自管道通信,值为“p”,否则为“.” (1.3.12, 1.2.7)
$proxy_protocol_addr
获取代理访问服务器的客户端地址,如果是直接访问,该值为空字符串。(1.5.12)
$query_string
同 $args
$realpath_root
当前请求的文档根目录或别名的真实路径,会将所有符号连接转换为真实路径。
$remote_addr
客户端地址
$remote_port
客户端端口
$remote_user
用于HTTP基础认证服务的用户名
$request
代表客户端的请求地址
$request_body
客户端的请求主体
此变量可在location中使用,将请求主体通过proxy_pass, fastcgi_pass, uwsgi_pass, 和 scgi_pass传递给下一级的代理服务器。
$request_body_file
将客户端请求主体保存在临时文件中。文件处理结束后,此文件需删除。如果需要之一开启此功能,需要设置client_body_in_file_only。如果将次文件传递给后端的代理服务器,需要禁用request body,即设置proxy_pass_request_body off,fastcgi_pass_request_body off, uwsgi_pass_request_body off, or scgi_pass_request_body off 。
$request_completion
如果请求成功,值为”OK”,如果请求未完成或者请求不是一个范围请求的最后一部分,则为空。
$request_filename
当前连接请求的文件路径,由root或alias指令与URI请求生成。
$request_length
请求的长度 (包括请求的地址, http请求头和请求主体) (1.3.12, 1.2.7)
$request_method
HTTP请求方法,通常为“GET”或“POST”
$request_time
处理客户端请求使用的时间 (1.3.9, 1.2.6); 从读取客户端的第一个字节开始计时。
$request_uri
这个变量等于包含一些客户端请求参数的原始URI,它无法修改,请查看$uri更改或重写URI,不包含主机名,例如:”/cnphp/test.php?arg=freemouse”。
$scheme
请求使用的Web协议, “http” 或 “https”
$sent_http_name
可以设置任意http响应头字段; 变量名中的后半部分“name”可以替换成任意响应头字段,如需要设置响应头Content-length,那么将“-”替换为下划线,大写字母替换为小写,形如:$sent_http_content_length 4096即可。
$server_addr
服务器端地址,需要注意的是:为了避免访问linux系统内核,应将ip地址提前设置在配置文件中。
$server_name
服务器名如www.baidu.com
$server_port
服务器端口
$server_protocol
服务器的HTTP版本, 通常为 “HTTP/1.0” 或 “HTTP/1.1”
$status
HTTP响应代码 (1.3.2, 1.2.2)
$tcpinfo_rtt, $tcpinfo_rttvar, $tcpinfo_snd_cwnd, $tcpinfo_rcv_space
客户端TCP连接的具体信息
$time_iso8601
服务器时间的ISO 8610格式 (1.3.12, 1.2.7)
$time_local
服务器时间(LOG Format 格式) (1.3.12, 1.2.7)
$uri
请求中的当前URI(不带请求参数,参数位于$args),可以不同于浏览器传递的$request_uri的值,它可以通过内部重定向,或者使用index指令进行修改,$uri不包含主机名,如”/foo/bar.html”。
服务器时间(LOG Format 格式) (1.3.12, 1.2.7)
$uri
请求中的当前URI(不带请求参数,参数位于$args),可以不同于浏览器传递的$request_uri的值,它可以通过内部重定向,或者使用index指令进行修改,$uri不包含主机名,如”/foo/bar.html”。
监控模块http_stub_status_modules
作用:监控Nginx客户端状态
作用域:server;location
|
|
- 配置语法:在一个server下配置
|
|
- 修改完之后,测试配置文件是否有错误
|
|
- 重载配置文件
|
|
- 再访问htttp://ip/stasus,出现一下
|
|
- nginx_status详解
|
|
模块http_random_index_module
作用:在主目录中选择一个随机主页
默认:关闭
作用域:location
- 配置语法:在location中配置
|
|
- 在/etc/nginx/html中新建一个html文件
- 重复上一小节的检查配置文件,重载配置文件,在浏览器访问,不断刷新,出现不同的页面
默认模块http_sub_module
作用:HTTP内容替换
常用选项:sub_filter string replacement;sub_filter_last_modified on|off;sub_filter_once on|off
作用域:http;server;location
-
配置语法
1 2 3 4 5 6location / { root /etc/nginx/html; index index.html index.htm; sub_filter 'nginx' 'NGINX'; #替换第一个nginx sub_filter_once off; #关闭之后,所有的nginx都会被替换 }
Nginx的请求访问限制
请求限制
-
连接频率限制:limit_conn_module
limit_conn_zone key zone=name:size,作用域:http
limit_conn zone number,作用域:http,server,location
-
请求频率限制:limit_req_module
limit_req_zone key zone=name:size rate=rate,http
limit_req zone=name,作用域:http,server,location
-
配置语法:
在http下配置,以客户端的ip地址作为key,对这个key进行限制,同时申请一个zone空间大小为1m用来存储访问的频次信息。$binary_remote_addr可以节省zone空间。rate=1r/s:表示允许相同标识的客户端的访问频次,这里限制的是每秒1次,即每秒只处理一个请求。
|
|
- 在localtion下配置:
|
|
limit_req zone=req_zon:使用配置好的rate的速率来处理数据
burst=3:设置一个大小为3的缓冲区当有大量请求(爆发)过来时,超过了访问频次限制的请求可以先放到这个缓冲区内等待,但是这个等待区里的位置只有3个,超过的请求会直接报503的错误然后返回。
nodelay:如果设置,会在瞬时提供处理(burst + rate)个请求的能力,请求超过(**burst + rate)**的时候就会直接返回503,永远不存在请求需要等待的情况。如果没有设置,则所有请求会依次等待排队
访问限制
基于IP的访问控制:http_access_module
-
常用选项:
allow address | CIDR | unix: | all。作用域: http,,server, location,limit_except
allow允许访问 ,address配置为IP地址
deny address | CIDR | unix: | all。作用域:http, server, location, limit_except
deny不允许访问 ,address配置为IP地址
-
在location下配置:
1 2 3 4 5 6location / { root html; deny 192.168.1.74;#也可以配置IP段:192.168.1.0/24 allow all; index show.html; }如上所示,location下的’/‘目录不允许IP为192.168.1.74的用户访问,其他地IP都可以访问。当192.168.1.74访问时,会出现403页面,不允许访问。
-
局限性:
由于http_access_module的访问控制是是针对客户端的IP来进行限制,凡是和nginx进行连接交互的都会被当作客户端,当真正的客户端与nginx之间有一下代理服务的时候,这种IP的控制就会失效。
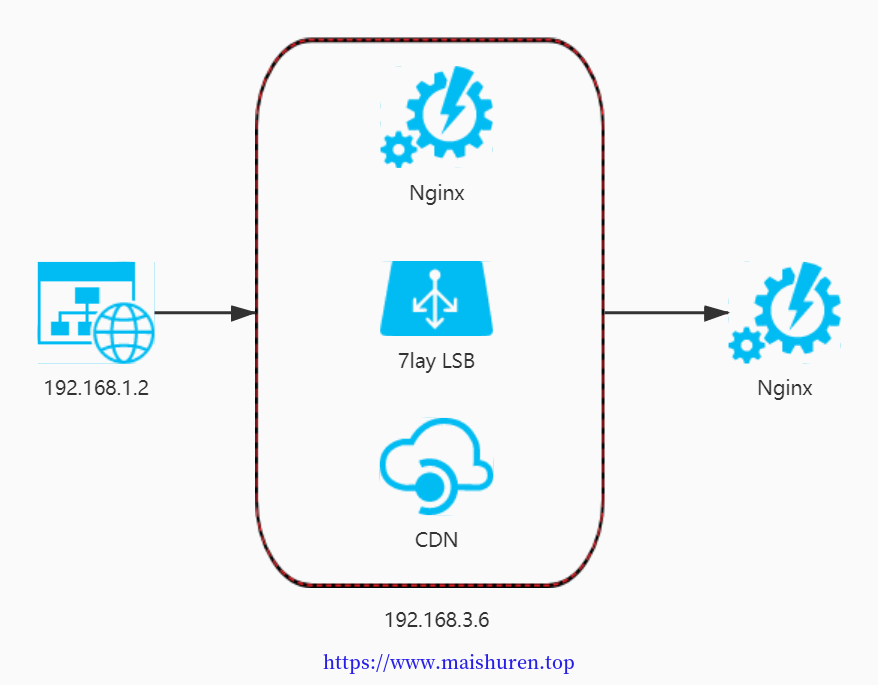
-
局限性解决方法总结:
方法一: 采用http头信息控制访问,如HTTP_X_FORWARD_FOR 方法二: 结合geo模块 方法三: 通过HTTP自定义变量传递
http_x_forwarded_for头信息控制访问 会更好的解决该问题,它要求访问时必须带上所有用到的ip的地址信息
|
|
基于用户的信任登录:http_auth_basic_module
-
常用选项:
auth_basic string | off。默认: auth_basic off。作用域:http, server, location, limit_except
auth_basic_user_file file。作用域: http, server, location, limit_except
-
配置:
|
|
- 在location下配置
|
|
再去访问,就会出现,认证框。虽然可以实现访问控制,但是用户信息依赖外部文件,操作管理机械,效率低下。所以可以Nginx结合LUA实现高效认证,Nginx和LDAR大同,利用nginx-auth-ldar模块